Overview of Renewable Energy
Renewable energy comes from natural sources that replenish over time, unlike finite fossil fuels. Solar and wind are prime examples of this shift to sustainable power. According to the International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA), renewable energy accounted for 29% of global electricity generation in 2020.
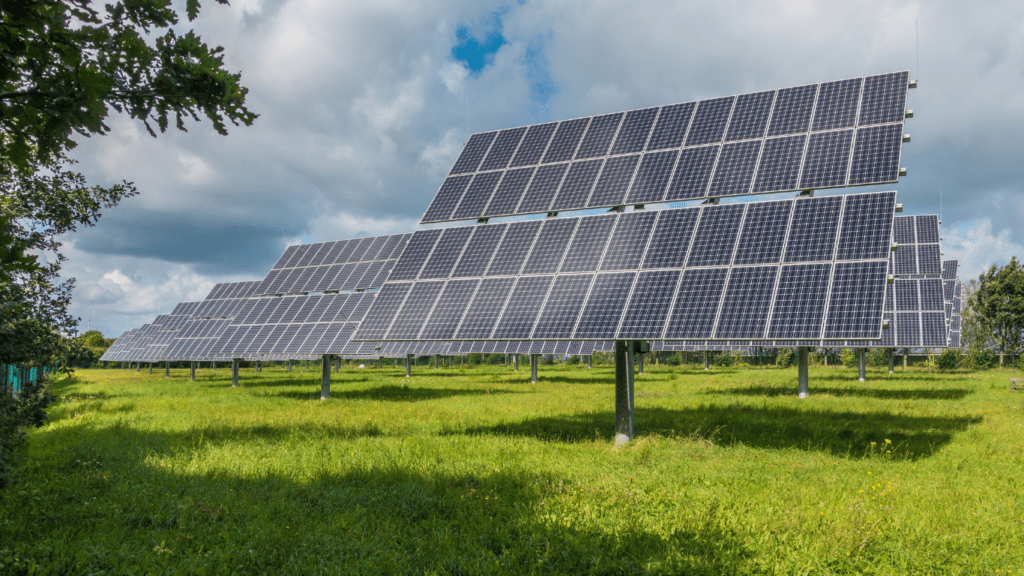
Solar energy harnesses sunlight, converting it into electricity using photovoltaic cells. It has seen exponential growth due to declining costs and increased efficiency. Solar panels now appear on residential rooftops, commercial buildings, and utility-scale solar farms.
Wind power converts kinetic energy from wind into electricity using turbines. Onshore and offshore wind farms are becoming more common due to technological advances and decreased costs. Wind power generated 7% of the world’s electricity in 2019, per IRENA.
Advantages of renewable energy include reduced carbon emissions and improved energy security. Renewable sources help combat climate change and offer stable energy prices, unaffected by geopolitical tensions or resource scarcity.
Governments worldwide support this transition through subsidies, tax incentives, and renewable energy targets. Policies like these help create favorable conditions for innovation and expansion in the renewable energy sector. Consequently, solar and wind power are vital to the global push for a greener, more sustainable future.
The Growth of Solar Power
Solar power is transforming the energy landscape at an impressive rate. It has become a cornerstone of renewable energy solutions, driven by continuous advancements and increasing adoption worldwide.
Technological Advancements
Solar power technology has advanced significantly over the past decades. Photovoltaic (PV) cells have evolved from bulky, inefficient systems to streamlined, highly efficient modules. Today’s PV cells convert sunlight into electricity with efficiency rates of over 20%, compared to less than 10% in the 1970s.
Innovations like bifacial panels, which capture sunlight on both sides, and thin-film technology, which uses less material, further enhance performance. Additionally, energy storage solutions, such as lithium-ion batteries, store surplus power for use when sunlight is unavailable, ensuring a consistent power supply.
Market Adoption and Trends
Adoption of solar power has surged as costs have plummeted. From 2010 to 2020, the price of solar PV panels dropped by about 89%, according to the International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA).
This cost reduction, coupled with government incentives, has made solar energy more accessible to homeowners, businesses, and large-scale utilities. Solar installations in residential areas, commercial buildings, and solar farms are increasingly common.
Utility-scale solar farms now supply significant portions of the grid. In 2020, solar power accounted for 3.1% of global electricity generation, demonstrating its growing market presence. Furthermore, emerging trends like solar-plus-storage and community solar projects enable broader participation and benefit-sharing.
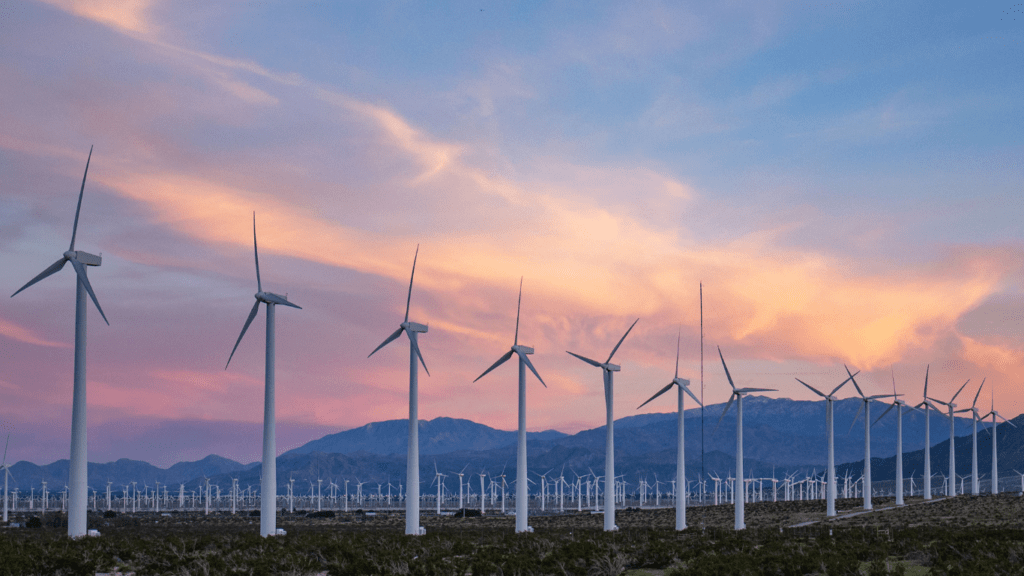
Wind Power Expansion
Wind power is rapidly gaining momentum worldwide, driven by technological advancements and increasing adoption rates. Let’s dive deeper into efficiency enhancements and global wind power adoption.
Efficiency Enhancements
Advances in turbine technology have dramatically improved the efficiency of wind power. Modern turbines are larger, with longer blades that capture more wind energy.
For example, the average turbine rotor diameter increased from 50 meters in 2000 to over 120 meters in 2020. This enhancement boosts energy output, making wind power more cost-competitive.
Grid integration techniques further enhance efficiency. Innovations like smart grids and energy storage systems ensure that wind-generated electricity is reliably distributed. It addresses one of the major challenges: variability in wind speed.
Global Wind Power Adoption

- Countries worldwide are embracing wind power.
- China leads the pack, with 288 GW of installed capacity in 2020.
- The US follows with 122 GW.
- Germany and India round out the top four with 62 GW and 38 GW respectively.
- Government policies play a significant role.
- Incentives such as feed-in tariffs, tax breaks, and renewable energy mandates stimulate investment.
- The European Union targets 32% renewable energy by 2030, propelling significant wind power growth.
- Investments are also pouring into offshore wind farms.
- These installations offer higher wind speeds and fewer space constraints, enhancing the attractiveness of wind energy for coastal nations.
- Wind power’s future looks promising, with ongoing advancements and widespread adoption reshaping the global energy landscape.
Economic and Environmental Benefits
Renewable energy sources like:
- solar power
- wind power
offer significant economic and environmental advantages. From cost savings to carbon reduction, these benefits make a compelling case for widespread adoption.
Cost-Effectiveness
Solar and wind energy have become more cost-effective over the years. Solar PV panel prices dropped by nearly 89% between 2010 and 2020, making solar installations more accessible. Wind power, too, saw cost reductions, with the average cost of electricity from new onshore wind projects dropping by 47% in the same period.
These decreases make renewable energy a financially viable option for homes and businesses. The falling costs also stimulate job growth, with renewable energy sectors creating jobs 12 times faster than the rest of the economy. For instance, the solar industry employed over 240,000 people in the US as of 2020.
Reducing Carbon Footprint
Solar and wind power play critical roles in reducing carbon emissions. Unlike fossil fuels, which emit large amounts of CO2, renewable energy sources generate electricity without releasing greenhouse gases. In 2019, wind power alone reduced carbon emissions by 1.1 gigatons globally, equivalent to taking 236 million cars off the road.
Similarly, solar installations in the US are estimated to offset 100 million metric tons of CO2 annually. These significant reductions help in combating climate change and promoting cleaner air. Renewable energy adoption also lessens reliance on oil and gas, further decreasing environmental impacts associated with extraction and transportation.
Challenges and Future Outlook
Renewable energy presents numerous benefits, but it comes with challenges that need addressing. Technological barriers and policy frameworks play significant roles in shaping the future of solar and wind power.
Technological Barriers
Technological barriers hinder the growth of solar and wind energy. One major issue is energy storage. Since solar and wind energy are intermittent, large-scale storage solutions are necessary for consistent energy supply. Current battery technologies like lithium-ion are expensive and have limited capacity, impacting their widespread adoption. Research and innovations in storage technologies, such as solid-state batteries and advanced flow batteries, aim to mitigate this challenge.
Grid integration also poses issues, especially for wind power. The variability of wind can cause fluctuations in power supply, necessitating advanced grid management systems. Smart grids and improved forecasting technologies help manage these fluctuations but require significant investments and technological advancements. Additionally, the efficiency of solar panels and wind turbines needs further improvement to maximize energy capture and reduce costs.
Policy and Regulation
Policy and regulatory frameworks significantly influence the advancement of renewable energy. Government policies, including subsidies and tax incentives, have driven the adoption of solar and wind power. However, inconsistent policies and regulatory uncertainties can hinder progress. For instance, sudden changes in subsidy schemes or tax incentives can disrupt investments and project timelines.
Zoning laws and permitting processes also affect renewable energy projects. Stringent regulations can delay project approvals and increase costs. Simplifying these processes while ensuring environmental and community considerations could accelerate deployment. Furthermore, international cooperation on policy harmonization can encourage cross-border investments and technology exchanges, fostering a more unified approach to renewable energy expansion.

 Patience Degarmonic was instrumental in building the community and health sections of News Flip Network, bringing a fresh perspective to the platform. Her focus on wellness content, along with her efforts in curating relevant and insightful articles, added depth to the site’s offerings. Degarmonic’s contributions ensured that readers not only stay informed about current events but also gain valuable tips for leading balanced and healthy lives.
Patience Degarmonic was instrumental in building the community and health sections of News Flip Network, bringing a fresh perspective to the platform. Her focus on wellness content, along with her efforts in curating relevant and insightful articles, added depth to the site’s offerings. Degarmonic’s contributions ensured that readers not only stay informed about current events but also gain valuable tips for leading balanced and healthy lives.